
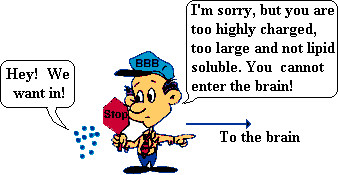
The blood-brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells which are cemented together by specialized intercelluar structures called tight junctions. Small molecules such as oxygen (O2) are allowed to pass - and rightly so since of course the brain needs oxygen! What the brain doesn't need is irregular concentrations of ions like potassium or sodium which play a role in keeping cells polarized - readied for action potentials.

No comments:
Post a Comment